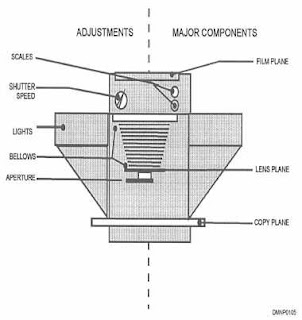
Tuesday, August 30, 2011
Thursday, July 28, 2011
color scanning practice
Wednesday, July 27, 2011
printing PDF's
Friday, July 15, 2011
Using the Nikon film scanner
Using the Nikon Film Scanner
1. Download the manual and save it as a PDF
http://www.nikonusa.com/pdf/manuals/noprint/LS5000_50_en_noprint.pdf
2. Go to pages 24-34
On page 35, This should be all set for you.
3. Then, pages 36-38.
4. Pages 40-46 has detailed information on the Scan Window, ICE, ROC, and GEM.
ICE, ROC and GEM need to be done in Preview.
ICE for scratches and dust
ICE normal may be sufficient. ICE fine may soften the image.
ICE does not work with conventional black and white film, but would work with chromogenic black and white. Not recommended for Kodachrome, since Kodachrome was not E6 slide processed.
ROC for restoring faded colors.
View in preview. It is powerful and may look unnatural.
GEM for grain.
Preview levels. Start at level 2?
ICE may need to be turned off.
Monday, July 11, 2011
lonnie

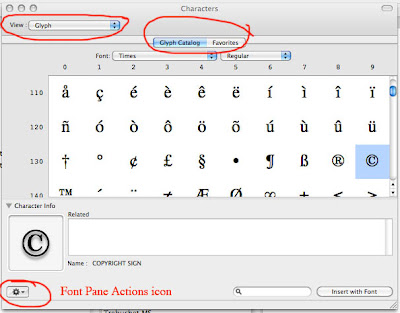
Adding Glyph to Character Palettes Favorites
Thursday, June 30, 2011
Tuesday, June 28, 2011
Saturday, June 25, 2011
scanning worksheet
Wednesday, June 22, 2011
Emerging Technologies
Presentation dates and topics:
Betty_Color changing
Wednesday, June 15, 2011
McNeely Piggott & Fox Public Relations
http://www.mpf.com/
Most computers are PC. The head designer uses PC.
75% of design work is print. Remainder is web and multi media.
The impact of technology..........
25-35 demo gets this from Internet (national) and Facebook (local)
They are curious about the future and the impact of technology. A need is how to tap into younger demographic that uses texting for information.
Teams work on projects. Teams meet once a week.
Task log.
Sunday, June 12, 2011
vocabulary simplified
Computer — comprised of:
a. hardware- it’s hard. You can drop it, break it, bump into it.
b. software- it’s invisible. It’s the programming code written on disks. You buy software like applications, fonts, games. It comes on a disk or you download from another computer to yours, like over the internet.
Operating system
Runs all the basic computer functions, like an engine in a car. You can have a car, but if you don’t have an engine it won’t go anywhere.
Drivers
Software that allows computer work with peripheral hardware, like printers and scanners. Must be installed, usually.
Applications
Programs that let you make stuff on the computer, like word processing, page layout, digital imaging.
Plug-ins
Small programs designed to enhance existing software with additional functions. They may cause problems when you go from one computer to another because you won't have the plug in on the other computer.
They may be called extensions.
CPU
Central processing unit. The chip that runs the show.
Also called a microprocessor.
Data bus
a combination of software, hardware, and electrical wiring that creates a way for all the different parts of your computer to communicate with each other. All the cables and wires connect to the bus.
Hard disk
Hardware pieces that hold data. Sort of like a filing cabinet.
RAM
Random access memory.
The word memory generally refers to RAM, which is temporary, volatile, storage space, as opposed to permanent storage space.
You might think of your computer’s hard disk as a filing cabinet, with each gigabyte or megabyte of space representing one drawer. The computer takes things out of the hard disk and places them on its desk, but its desk is called random access memory or RAM. So when you open an application like a word processing application, the computer gets a copy of that application out and puts the copy into memory, or places it on the desk. Sort of like putting a typewriter on the desk.
So you crash if too much stuff is on the desk.
Whatever you did in RAM goes away, if not saved, when you turn off the computer.
ROM
Read only memory.
System information that is built into the ROM chips inside the computer. This is information that gets the system up and running.
How is screen size measured?
a. diagonally in inches
b. number of pixels, width by height
Text file formats:
1. Open, meaning they can move between Mac & PC and software.
ASCII and RTF are examples of “open format”
2. Program-specific, such as Microsoft Word.
Program specific formats lose formatting when you transfer to a Mac.
ASCII may not have all the information necessary, especially missing may be numbers and special characters.
RTF is probably the best choice. Keeps typographic information.
Text Edit review
Saturday, June 11, 2011
Virtual Keyboard & Character Viewer in Macs
Go to System Preferences>International>Input Menu.
Check Keyboard Viewer and Character Palette.
Check Show input menu in menu bar at the bottom of the window.
The icon will appear in upper right hand section of the menu bar. Usually next to the Volume icon.
You can show the keyboard with Show Keyboard Viewer
You can show the characters with Show Character Viewer. At the Character Viewer, you can select a character, and then click on insert to place it in you document.
Saturday, May 21, 2011
lonnie



